
International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering (IJRTE)
ISSN: 2277-3878 (Online), Volume-8, Issue-1, May 2019
1220
Published By:
Blue Eyes Intelligence Engineering &
Sciences Publication
Retrieval Number: A9218058119/19©BEIESP
Journal Website: www.ijrte.org
Moving From Cash to Cashless Economy: - A
Study of Consumer Perception Towards Digital
Transactions
Richa Goel, Seema Sahai, Anita Vinaik, Vikas Garg
Abstract: In this era, we can see a very significant level of
change in the means of making and receiving payments. Due to
constant level of technological infrastructure and policy changes,
there has been an increase in the number of modes of payments.
Cashless economy is the future of Indian economy where there
will be no physical flow of cash. All the payments will be made
and received in the virtual world. Cashless economy got popular
after demonetization where plastic money was widely used. The
study is aimed towards studying the level of awareness among the
citizens about cashless economy. The study also helps in
determining the factors which influence the people to switch
from cash towards cashless payments and what are the benefits
people avail by using other means of payments.The primary data
was collected by distributing questionnaires to 280 respondents,
who have been using any digital mode of payment. Data is
collected from students, working professionals and business class
people. The questionnaire asks questions about the benefits
people avail while using digital payment methods and what are
the various factors which influence the people to use digital
payment methods and what are the risks they face associated with
digital payments.After the research conducted we can say that the
working professionals and business class people use digital
payment methods more. There are various factors which
influence the people to shift such as offers, cashback etc. There is
still a long run for India to be cashless to full extent as the
government needs to develop a smooth and secure infrastructure.
Index terms: Cashless economy, technological development,
demonetization, digital payment methods.
I. INTRODUCTION
The prime minister of India, on 8th November, 2016
demonetized the two largest denominations of currency
notes of INR 500 and INR 1000, which were ceased with
immediate effect with a few exceptions. The entire nation
was in a state of shock because such a huge render was
declared invalid in just one announcement and it was not the
first time the government of India has not taken such a step
earlier. Indian government took this step in 1946 and 1978
but in 2016 it faced a lot of criticism as people were left
with only INR 100 notes or less denomination to transact
with.
Revised Manuscript Received on 30 May 2019.
* Correspondence Author
Richa Goel, AIBS, Amity University,NOIDA, India
Seema Sahai, AIBS, Amity University,NOIDA, India
Anita Vinaik, ABS, Amity University,NOIDA, India
Vikas Garg, Amity University Greater NOIDA, India
© The Authors. Published by Blue Eyes Intelligence Engineering and
Sciences Publication (BEIESP). This is an open access article under the
CC-BY-NC-ND license http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
The main aim of this step was aimed to attack on counterfeit
currency, currency used for terrorist financing, black money
and corruption. Not only this the Prime Minister of India is
also working towards digitization of India (DIGITAL
INDIA). Thus, both moves DEMONETISATION and
DIGITIZATION if worked upon effectively will help the
Indian Economy to become Cashless Economy.Cashless
Economy refers to the term where the physical flow of
currency notes and coins are replaced with digital flow of
money, which includes use of plastic money, digital means
and over the net transactions. Such a replacement doesn’t
mean immediate removal of currency notes but slowly and
gradually expelling of paper currency by means of following
a proper procedure.Physical money means the paper
currency notes and coins issued by the government as legal
tender. Plastic money involves the use of plastic cards such
as debit cards, credit cards, pre-paid cards, contact less cards
etc. Electronic payment modes include all kinds of mobile
wallets and payments made done through smart phones,
laptops etc.
A. AROUND THE WORLD SCENARIO
As per the survey conducted by CNBC most cashless
countries are:
Germany:
Share of non-cash payments: 76%
Share of people using debit cards:88%
South Korea:
Share of non-cash payments:70%
Share of people using debit cards:58%
United States of America:
Share of non-cash payments:80%
Share of people using debit cards:72%
The Netherlands:
Share of non-cash payments:85%
Share of people using debit cards:98%
Australia:
Share of non-cash payments:86%
Share of people using debit cards:7
Sweden:
Share of non-cash payments:89%
Share of people using debit cards:96%

Moving From Cash to Cashless Economy: - A Study of Consumer Perception Towards Digital
Transactions
1221
Retrieval Number: A9218058119/19©BEIESP
Journal Website: www.ijrte.org
Published By:
Blue Eyes Intelligence Engineering &
Sciences Publication
United Kingdom:
Share of non-cash payments:89%
Share of people using debit cards:88%
Canada:
Share of non-cash payments:90%
Share of people using debit cards:88%
France:
Share of non-cash payments:92%
Share of people using debit cards:69%
Belgium:
Share of non-cash payments:93%
Share of people using debit cards:86%
B. METHODS OF DIGITAL PAYMENTS IN
INDIA
Banking Cards: These includes all types of plastic cards
such as credit card, debit card, cash card, travel card etc.
they provide 2 factor authentications for a secure
transaction.
USSD: Unstructured Supplementary Service Data is an
innovative of making payments without the use of internet
and smartphone. The payments can be made by a feature
phone by dialling *99#.
AEPS: Aadhar Enabled Payment System is a means by
which a person can make payments at the point of sale by
Aadhar authentication.
UPI: Unified Payment Interface powers multiple bank
accounts into a single mobile application, merging all or
some of the banking services.
Mobile Wallets: It is a means of carrying cash in digital
format. Credit card or debit card can be linked to the mobile
wallet for making payments or some money can be loaded
into the mobile wallet.
Internet Banking: It is a medium through which various
banking services like NEFT, RTGS, ECS, IMPS etc. can be
availed over the institution’s website.
Mobile Banking: It is a service provided by banks providing
its customers a platform to conduct various banking services
by use of their mobile phones or tablets through the apps
provided by the bank.
C. STRENGTHS OF INDIA GOING CASHLESS
A planned strategy: The government of India followed a
detail criterion by first SIT on black money, then Jan Dhan
Yojana which was followed by tracking on foreign accounts
and money hoarders. Then, the income declaration scheme
and finally, demonetization.
Financial inclusion: The government of India is focussing
on reaching all the corner and to every citizen. Many bank
accounts were created throughout the country as an initiative
taken up by government.
Steps taken by Government:
Launch of BHIM app for smartphone users based
on UPI.
Launch of Aadhar merchant pay.
Direct benefit transfer
D. WEAKNESS FACED BY INDIA
Cash is the dominating means of payment in the
Indian economy.
There is 24X7 electricity in India.
E-illiteracy is also a major weakness.
Smartphone market is still untapped.
Lack of technological infrastructure.
Sluggish economy.
E. OPPORTUNITIES AVAILABLE WITH INDIA
AFTER GOING CASHLESS
Curbing black money- Going cashless will bring an
end to the parallel economy running by black
money.
Tax collection- With digitization, tax collection
will be made easy.
Reduced real estate- going cashless will ensure
only payment in white money.
End of corruption- Going cashless will ensure a
proper check on bank accounts, which will reduce
the system of bribery.
F. THREAT WITH GOING CASHLESS
Threat of cyber-crimes.
Threat of loss of database.
Threat of data encryption.
Cash is considered the most convenient and fastest
means of payment.
It is very difficult to gain trust and faith among
Indians, as there are constant ups and downs in the
economy.
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
Mr. Pradeep H. Tawade (2017), “Future and scope of
cashless economy in India.” This paper helps in assessing
the future trends and the impact of going cashless in the
Indian economic scenario. After the study was conducted it
was seen that the Government of India should consider
many more steps in digitalizing India. And payment
methods should be made more secure and risk-free.
Dhanda and Arora (2017), Genesis of cashless society: A
study on growing acceptability towards plastic money. This
paper is aimed towards studying the factors responsible for
the rapid increase in acceptability of plastic card in the
recent years. After the study was conducted it was seen that
use of plastic cards is a matter of great pride among
teenagers and is considered safe and free from any frauds.

International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering (IJRTE)
ISSN: 2277-3878 (Online), Volume-8, Issue-1, May 2019
1222
Published By:
Blue Eyes Intelligence Engineering &
Sciences Publication
Retrieval Number: A9218058119/19©BEIESP
Journal Website: www.ijrte.org
Dr. Rashmi Gujrati (2017), India’s march towards faceless,
paperless, cashless economy. The paper is aimed towards
creating a sense of awareness about cashless economy, its
benefits, challenges and the steps taken by government
toward cashless economy. After the research conducted it
was seen that cashless economy comes with various benefits
but brings in a lot more challenges with it.
Dr. Asha Sharma (2017), Potential for cashless economy in
India. The study was conducted to find the scope of India
becoming a cashless economy, challenges and opportunities
related to cashless economy. The study shows that there is a
significant scope of Cashless India as we can abolish various
problems we face today but we must be prepared for the
challenges and problems which cashless economy will
bring.
Dominic, Saranya, and Rajani (2018), A study on
transformation in behaviour of individual towards cashless
economy. The study is aimed towards studying the
behavioural changes in individual towards cashless
economy. After the study conducted it was seen that many
individuals have already moved or are moving towards a
cashless nation but there is still a long way for India to
become cashless.
Mr. Bharat Khurana (2015), Dream of cashless India:
Benefits and challenges. The paper studies the benefits and
challenges India might face if it becomes a cashless nation.
It also helps in assessing the meaning of digital India and
steps taken by government towards achieving the dream of
cashless India. After the study no matter how much the
government had done for fulfilling the dream of digital India
but there is still a lot more that can be done to achieve that
dream.
Metri and Jindappa (2017), Impact of cashless economy on
common man in India. The study focusses on effect of going
cashless on a common man living in India and the
challenges related to going cashless. The study shows that
India can never turn into a fully cashless economy as cash
has been the dominating factor and always will be. Going
cashless will only be feasible for a very small section of the
society but not the whole nation.
Kumari and Khanna (2017), Cashless payment: a
behavioural change to an economic growth. The paper aims
to study how a behavioural change led to an economic
growth in the Indian economic scenario. After the study
conducted it was seen that various factors were responsible
for such a change as people were finding various benefits
and opportunities by adopting such a change.
Felix, Rebecca and Igbinoba (2015), Appraisal of the
impact of e-banking and cashless society in the Nigerian
economy. The paper was aimed towards understanding the
impact of e-banking and cashless society on the people of
Nigeria. But after the study was conducted it was seen that
most of Nigerian citizens were not at all aware of such
concepts and those who were aware were not fully using
such facilities and there was no infrastructure development
before implementing such changes.
Kousalya and Shankar (2018), Cashless
economy/transaction. The paper was focussed towards
understanding the impact of cashless economy and its
importance in India. After the research conducted it was
seen that the introduction of cashless economy in India will
bring about a positive impact on the financial sector and will
help in modernisation of the payment system in India.
Kokila and Ushadevi (2017), A study on consumer
behaviour on cashless transaction in U.T. of Puducherry.The
paper was focussed towards understanding the awareness
and trust among the customers about cashless transactions. It
was seen that people were aware about the cashless
transaction but were still in doubt with implementing the
same in daily routine.
Thomas and Krishnamurthy (2017), Cashless rural
economy- a dream or reality. The study is focussed towards
understanding the impact of demonetisation on rural India
and to keep a check on the government initiatives to make
rural market a cashless economy. The studies show that the
government of India should initiate various schemes to
make the dream of cashless economy a reality.
Shrikala K.K. (2017), Cashless Transaction: Opportunities
and Challenges with special reference to Kodagu district of
Karnataka. The paper is aimed to find the opportunities
available in the rural part of India and the challenges which
may be faced while moving towards a cashless economy. It
was seen that there are many opportunities and every
opportunity come with its own challenges, but they can be
avoided with proper implementation.
Shendge, Shelar and Kapase (2017), Impact and
importance of Cashless Transaction in India. The paper
focuses on impact and importance of cashless transactions in
India. The study shows that if India becomes a cashless
economy there will be both positive and negative impact,
but negative impacts can be overlooked if the gain from
positive impact is considered.
Garg and Panchal (2017), Study on Introduction of
cashless economy in India 2016: Benefits & challenges. The
study focusses on finding benefits and challenges related to
cashless economy in India. The study shows that there are
various benefits related to cashless economy and various
challenges related to the cashless economy.
Akinola (2012), Cashless Society, Problems and
Prospects, Data Mining Research Potentials. The is focused
on understanding the cashless society and the problems
related to the same in Nigeria. The study shows that cashless
society will face a lot of challenges and criticism by the
citizens of Nigeria.
Bindra and Bindiya (2017), Going Cashless: stepping
towards Digital India. The study is focussed to find out
benefits, challenges and the growth prospects in India on the
path of moving towards digital India. The study shows that
digital India will bring a huge growth in the GDP of India
and will also have other benefits are the society and the
economy as well.
Thilagavathy and Santhi (2017), Impact and importance of
Cashless Transaction in India. The paper focuses on impact
and importance of cashless transactions in India. The study
shows that if India becomes a cashless economy there will
be both positive and negative impact, but negative impacts
can be overlooked if the gain from positive impact is
considered.

Moving From Cash to Cashless Economy: - A Study of Consumer Perception Towards Digital
Transactions
1223
Retrieval Number: A9218058119/19©BEIESP
Journal Website: www.ijrte.org
Published By:
Blue Eyes Intelligence Engineering &
Sciences Publication
Sharad Malhotra (2017), Impact of Cashless Society for the
Economic Growth in India. The paper focuses on impact
and importance of cashless transactions in India. The study
shows that if India becomes a cashless economy there will
be both positive and negative impact, but negative impacts
can be overlooked if the gain from positive impact is
considered. There would be lower costs and keep a check on
financial crimes and TAX frauds.
III. OBJECTIVES
A. PRIMARY OBJECTIVES
To study consumer awareness on cashless
transactions.
To assess the customer trust and confidence in
cashless transactions.
To study benefits of cashless economy.
To analyse future trends of cashless transactions.
B. SECONDARY OBJECTIVES
To understand the factors influencing the customer
moving towards cashless economy.
To illustrate the steps taken by government to fulfil
the dream of digital India.
To assess the preparedness of Indian Government
for implementing the cashless economy.
To study the socio-economic impact of cashless
economy on the society.
IV. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This study reviews literature chosen with the primary as
well as secondary data.
A. Research Design:
The research is analytical and descriptive in nature. The
researcher for the purpose here had made use of primary
data and secondary data. The researcher has made use of
close ended questionnaire where sample of 280 was used.
The data was collected and was analysed by using SPSS
Software.
Secondary sources were also used with respect to Review
of Literature, Journals and articles.
Descriptive Statistics was done by using Mean, Standard
Deviation, Frequency and inferential statistics was used like
correlation, regression and ANOVA.
B. Sources of Data
The data required for doing the research has been collected
mainly by using primary and secondary sources. The
primary sources include the questionnaire. The secondary
source includes the various journals, research paper and
internet websites.
C. Size of Sample
The study has been conducted by using the sample of 280.
V. RESEARCH FINDINGS AND ANALYSIS
SURVEY
A. RESPONSE RATE
This table shows the No. of questionnaires and their validity
received for analysis
B. FINDING OUT DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS
FREQUENCIES
This table shows the number of respondents and their
demographic information
C. RELIABILITY
The table above shows the degree of the questionnaire’s
reliability. The value of alpha is 0.896 which is more than
0.6. This shows that the data is reliable for further analysis.
D. USING MEAN AND STANDARD DEVIATION

International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering (IJRTE)
ISSN: 2277-3878 (Online), Volume-8, Issue-1, May 2019
1224
Published By:
Blue Eyes Intelligence Engineering &
Sciences Publication
Retrieval Number: A9218058119/19©BEIESP
Journal Website: www.ijrte.org
As we can see the mean in this table lies between 1 and 3,
it shows that the respondents have a positive approach i.e.
they opted to agree towards the parameters. Standard
deviation shows the degree at which the mean is deviating
from the actual mean.
E. HYPOTHESIS
There is no significant difference between level of
consumer trust and confidence in their cashless
transactions.
There are no significant benefits of cashless
economy to public.
There is no significant difference between level of
awareness among consumers and their cashless
transactions.
There is no significant potential level of cashless
economy in India.
F. CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
G. HYPOTHESIS-1
H0: There is significant difference between level of
consumer trust and confidence in their cashless transactions.
H1: There is no significant difference between level of
consumer trust and confidence in their cashless transactions.
This table shows the relationship between trust and
confidence.
This table shows the significant relationship of Trust and
Confidence, where trust is dependent, and Confidence is
independent.
The test shows that there is a significant relationship
between the level of trust and level of confidence.
So, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
H. HYPOTHESIS-2
H0: There is no significant relationship between gender and
benefits of cashless economy to public.
H2: There is a significant relationship between gender and
benefits of cashless economy to public.
This table shows the relationship between Gender and
Benefits.
Moving From Cash to Cashless Economy: - A Study of Consumer Perception Towards Digital
Transactions
1225
Retrieval Number: A9218058119/19©BEIESP
Journal Website: www.ijrte.org
Published By:
Blue Eyes Intelligence Engineering &
Sciences Publication
This table shows the significant relationship of Gender and
Benefit, where Gender is dependent, and Benefits is
independent.
Coefficients
Model
Unstandardized Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
t
Sig.
B
Std. Error
Beta
1
(Constant)
1.499
.049
30.328
.000
B
-.025
.021
-.070
-1.161
.247
a. Dependent Variable: Gender
The test shows that there is a significant relationship
between the gender and level of benefits from the cashless
society.
So, we reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternate
hypothesis.
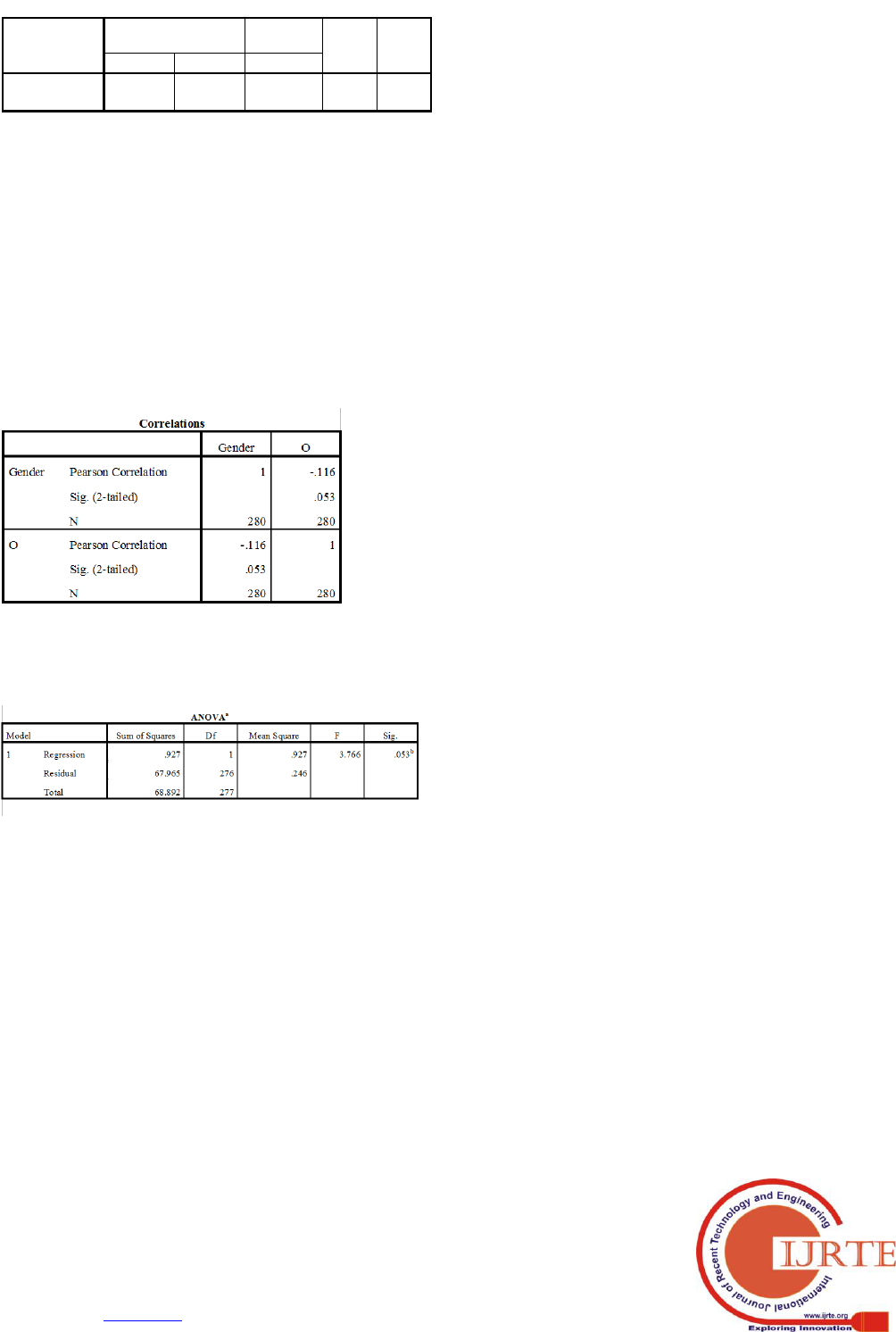
I. HYPOTHESIS-3
H0: There is no significant relationship between gender and
the level of optimism towards cashless transactions.
H3: There is a significant relationship between gender and
the level of optimism towards cashless transactions.
This table shows the relationship between Gender and their
level of optimism towards cashless transactions. The
relationship is negative in nature.
The test shows that there is no significant relationship
between the gender and level of optimism towards cashless
transactions.
So we fail to reject the null hypothesis
VI. CONCLUSION
We can conclude that there is a long way for India to
become a cashless economy. People still lack trust and
confidence while using digital payment methods. A lot of
development in the field of infrastructure is required to
make the dream of Digital India a reality. There are many
people who are still not aware about the cashless economy
not only in India but outside of India. Government has faced
a lot of criticism in the past from the public for the various
plans implemented on the public. There are a lot of
challenges in fulfilling the dream of digital India but in the
long run cashless economy will help in growth and will
bring a lot of benefits and opportunities with it.
Few of the major finding according to this study are:
There are still a lot of people who do not use any
kind of digital payment method.
There are a lot of scope in the future for cashless
society.
People are mostly influenced by convenience and
offers provided for switching to cashless modes of
payments.
There is still a lot to be done to digitalise India.
People don’t feel safe sharing their financial and
personal information over the internet.
People face various problems while using digital
payment methods.
VII. KEY SUGGESTIONS
Government of India should try to educate people
about the benefits of going cashless before taking
any crucial steps.
They should also be able to implement their plans
properly and without troubling the public.
They should also tell about the opportunities which
the public will get if they become digital.
People should try and use any digital payment
method at least once.
Government should develop infrastructure to cope
up with any policy change or a plan
implementation beforehand.
People and government should work together to
develop infrastructure and technology to digitalize
India.
REFERENCES
1. Mr. Pradeep H. Tawade (2017), Future and scope of cashless economy
in India
2. Dhanda and Arora (2017), Genesis of cashless society: A study on
growing acceptability towards plastic money
3. Dr. Rashmi Gujrati (2017), India’s march towards faceless, paperless,
cashless economy
4. Dr. Asha Sharma (2017), Potential for cashless economy in India
5. Dominic, Saranya, and Rajani (2018), A study on transformation in
behaviour of individual towards cashless economy
6. Mr. Bharat Khurana (2015), Dream of cashless India: Benefits and
challenges
7. Metri and Jindappa (2017), Impact of cashless economy on common
man in India
8. Kumari and Khanna (2017), Cashless payment: a behavioural change to
an economic growth
9. Felix, Rebecca and Igbinoba (2015), Appraisal of the impact of e-
banking and cashless society in the Nigerian economy
10. Kousalya and Shankar(2018), Cashless economy/transaction
11. Kokila and Ushadevi(2017), A study on consumer behaviour on
cashless transaction in U.T. of Puducherry
12. Thomas and Krishnamurthy (2017), Cashless rural economy- a dream
or reality
13. Shrikala K.K. (2017), Cashless Transaction: Opportunities and
Challenges with special reference to Kodagu district of Karnataka
14. Shendge, Shelar and Kapase (2017), Impact and importance of
Cashless Transaction in India
15. Garg and Panchal (2017), Study on Introduction of cashless economy
in India 2016: Benefits & challenge

International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering (IJRTE)
ISSN: 2277-3878 (Online), Volume-8, Issue-1, May 2019
1226
Published By:
Blue Eyes Intelligence Engineering &
Sciences Publication
Retrieval Number: A9218058119/19©BEIESP
Journal Website: www.ijrte.org
AUTHORS PROFILE
Dr. Richa Goel is Assistant Professor-Economics
and International Business at Amity International
Business School, Amity University Noida. She is a
Ph.D. in Management and has a journey of almost
18 years in academic and consistently striving to
create a challenging and engaging learning
environment where students become life-long
scholars and learners. Imparting lectures using
different teaching strategies , she is an avid teacher, researcher, and mentor.
She has to her credit a number of publications in reputed national and
international journals accompanied with participation in conferences. She is
serving as a member of review committee for conferences journals and
acting as Lead Editor of Annual International Referred Journal and
Research Coordinator with Amity International Business School. Her area
of interest includes Economics, Business Law, Human Resource
Management and Diversity Management.
Dr. Seema Sahai is Associate Professor in IT &
Operations at Amity International Business School,
Amity University Noida. She is a Ph.D. in
Management and has a journey of 23 years in
academic and consistently striving to create a
challenging and engaging learning environment
She has to her credit a number of publications in
reputed national and international journals accompanied with participation
in conferences. She has a corporate experience of 2 years and has many
projects to her credit.
Dr. Anita venaik with 19 years of work experience in
academics and 4 years in corporates. presently
working as professor at Amity business school .has
written 11 text books in Various subjects in IT
having 12 case studies published in European case
centre also more that 30 research papers in Various
national and international journals
Dr. Vikas Garg is a doctorate in commerce and
management from CCS University, Meerut. He is
currently working as an assistant HOD at Amity
Business School, Amity University Greater Noida
Campus. He is UGC NET qualified. With past
academic experience of 15 years, he has an expertise
in accounting and finance. His areas ofinterests are
financial markets, financial reporting and analysis. He
is associated with several Universities as an external guide for research
scholars. He is lifetime member of Indian Commerce Association, Indian
Accounting Association, Indian ManagementAssociation. He is certified in
Customer Relationship Management from IIM, Bangalore. As a Professor
of Amity University, has been an efficient researcher who has published
many research papers in various international and national journals. He is
highly efficient in different spheres of work and producing quality work.
He has in depth knowledge in the area of finance and accounting and has
been consistent performer in delivering accuracy in his tasks. He has
organized many seminars and workshops at different. He is very good team
leader and always performs the task with creativity.
